Exploring the World of Power Tools: Types, Uses, and Safety Tips
Power tools are essential in various industries and DIY projects. They offer increased efficiency and productivity compared to manual tools.
Types of Power Tools:
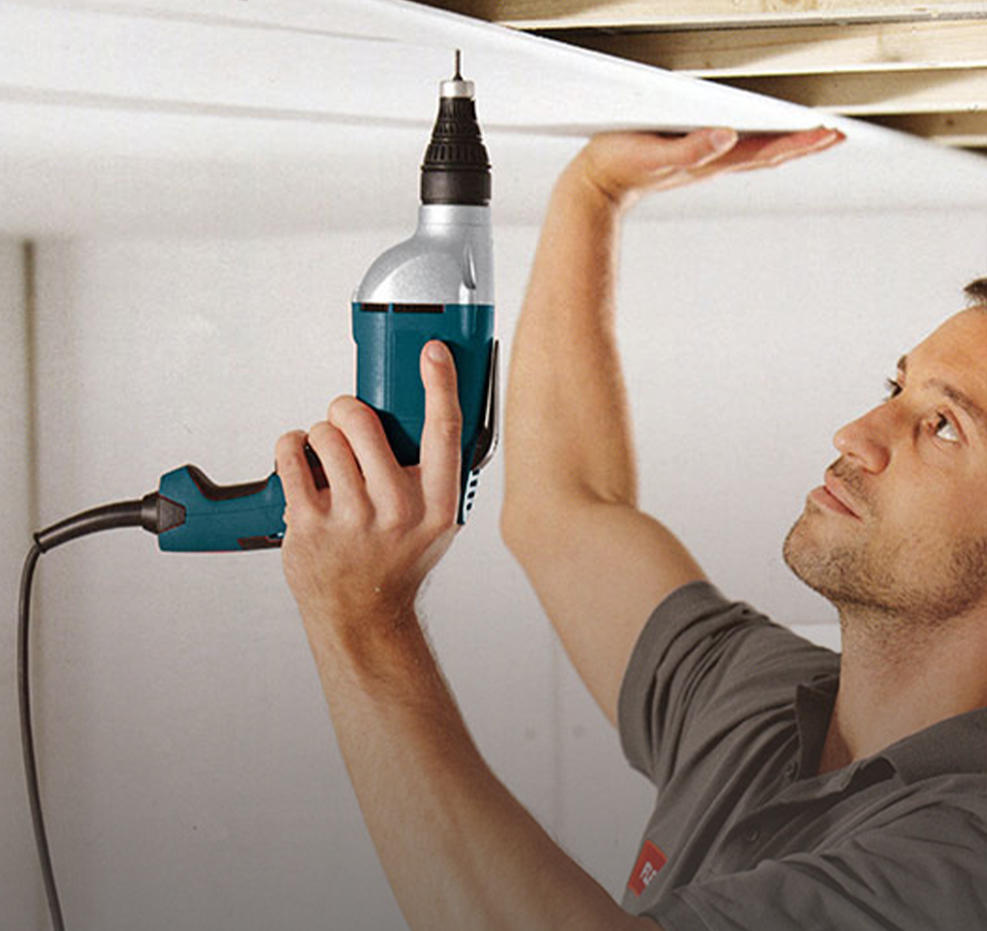
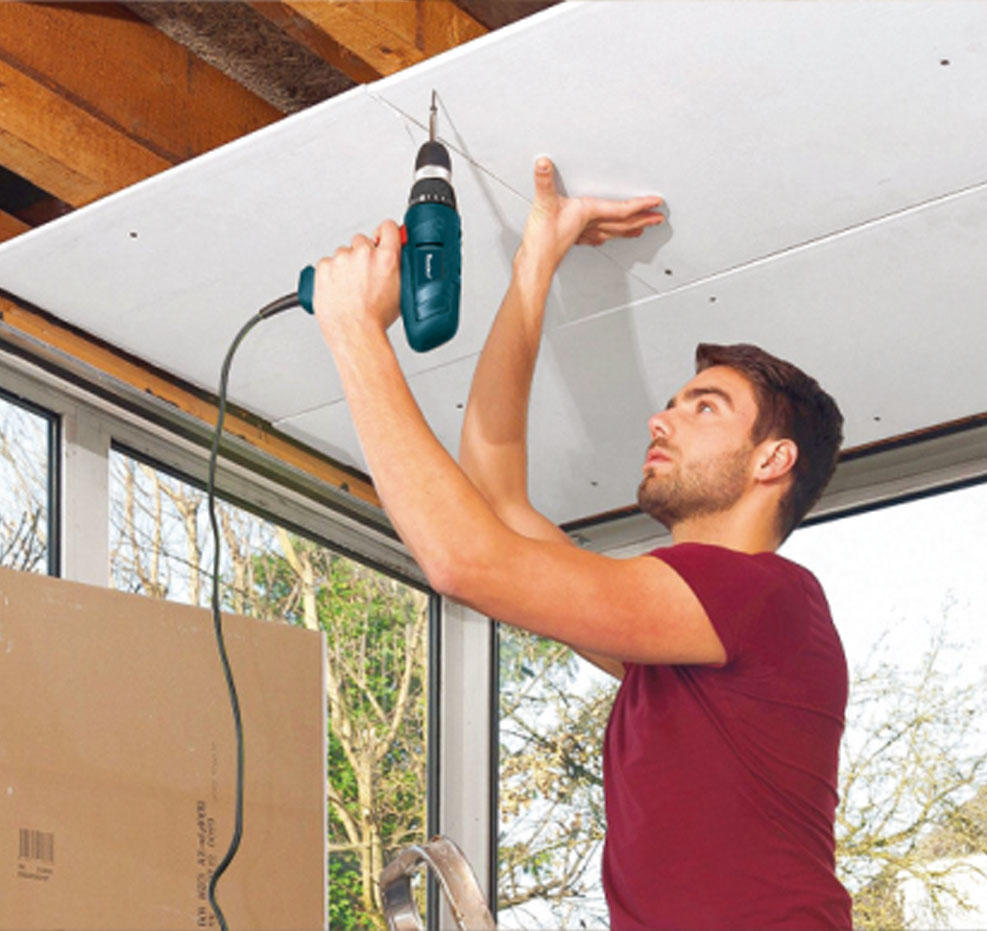
Drills: Used for making holes in various materials, drills come in different sizes and types, such as cordless drills, hammer drills, and impact drills.
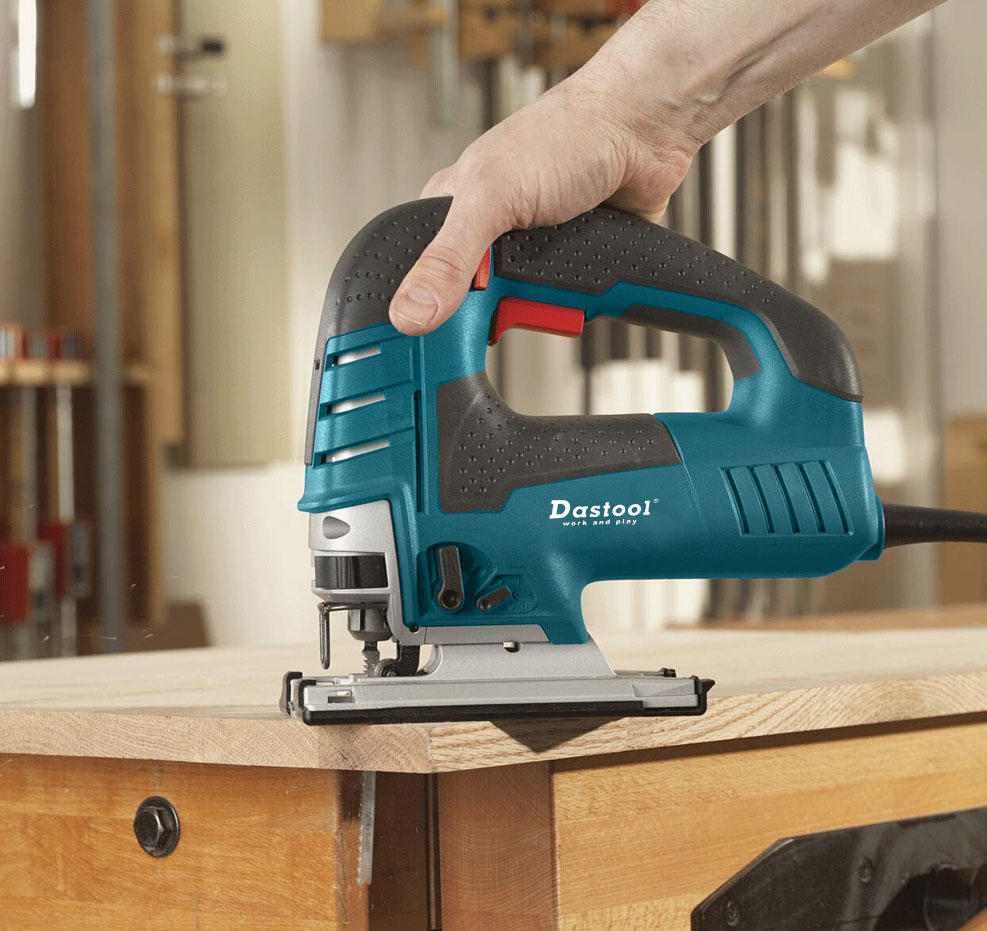
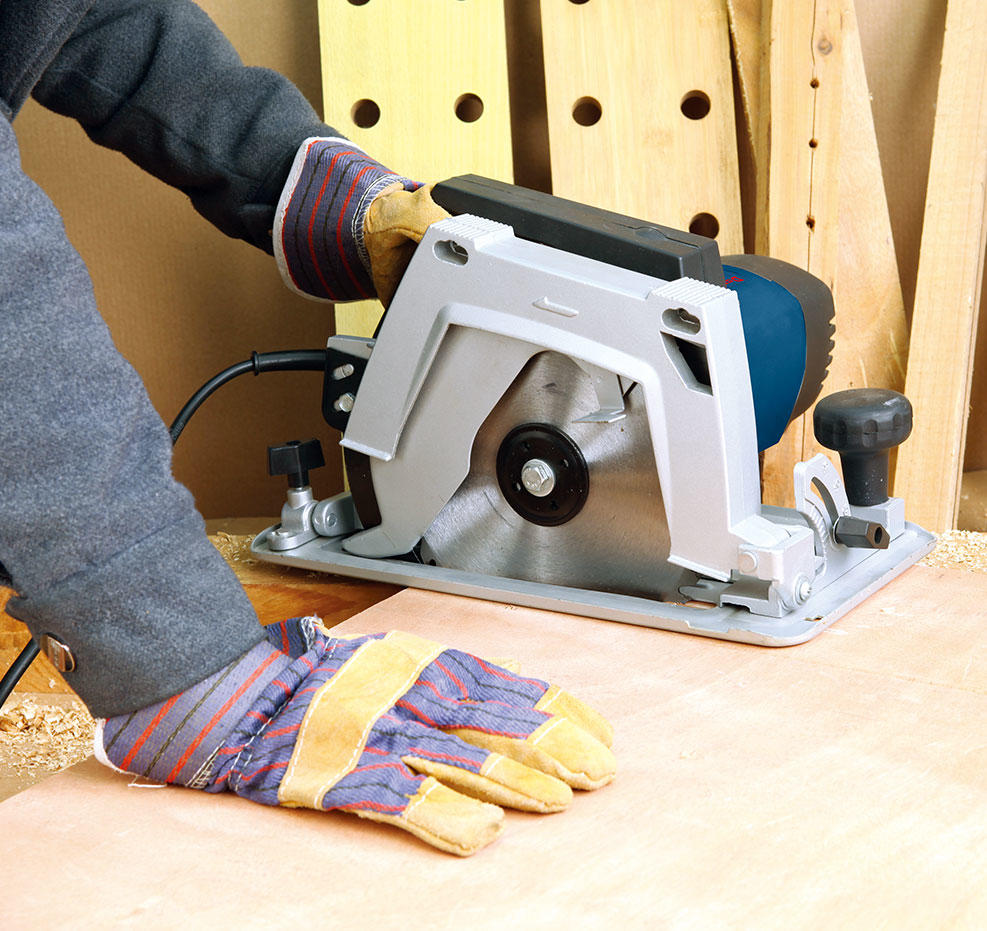
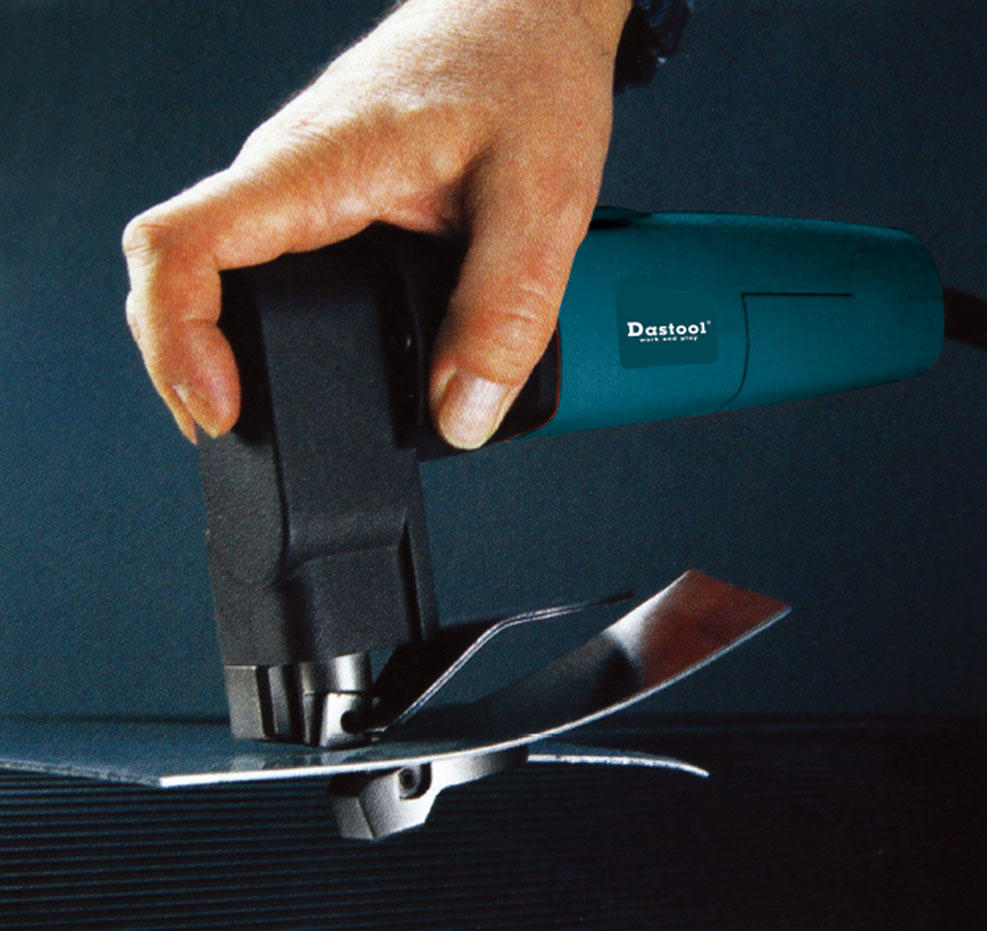
Saws: Power saws are available in various forms, including circular saws, jigsaws, reciprocating saws, and band saws. They are used for cutting wood, metal, plastic, and other materials.
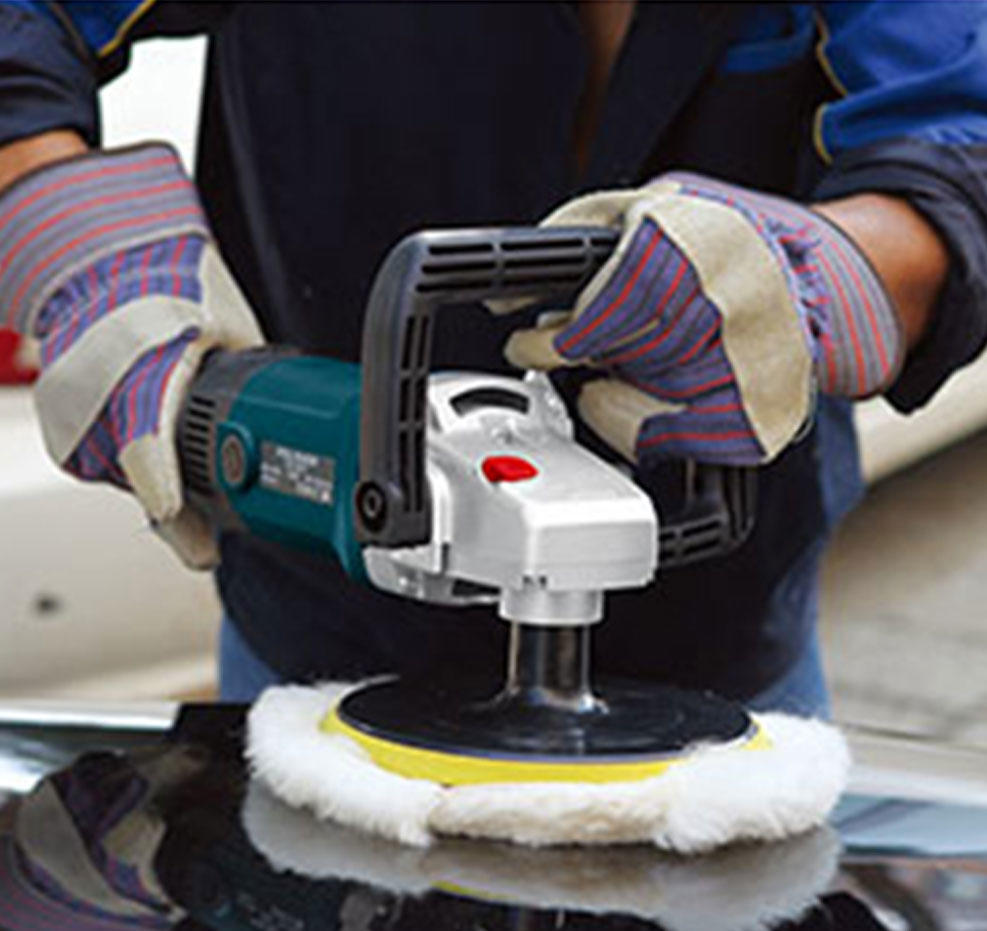
Sanders: Sanders are used to smoothen surfaces by removing paint, varnish, or rough edges. Common types include belt sanders, orbital sanders, and detail sanders.
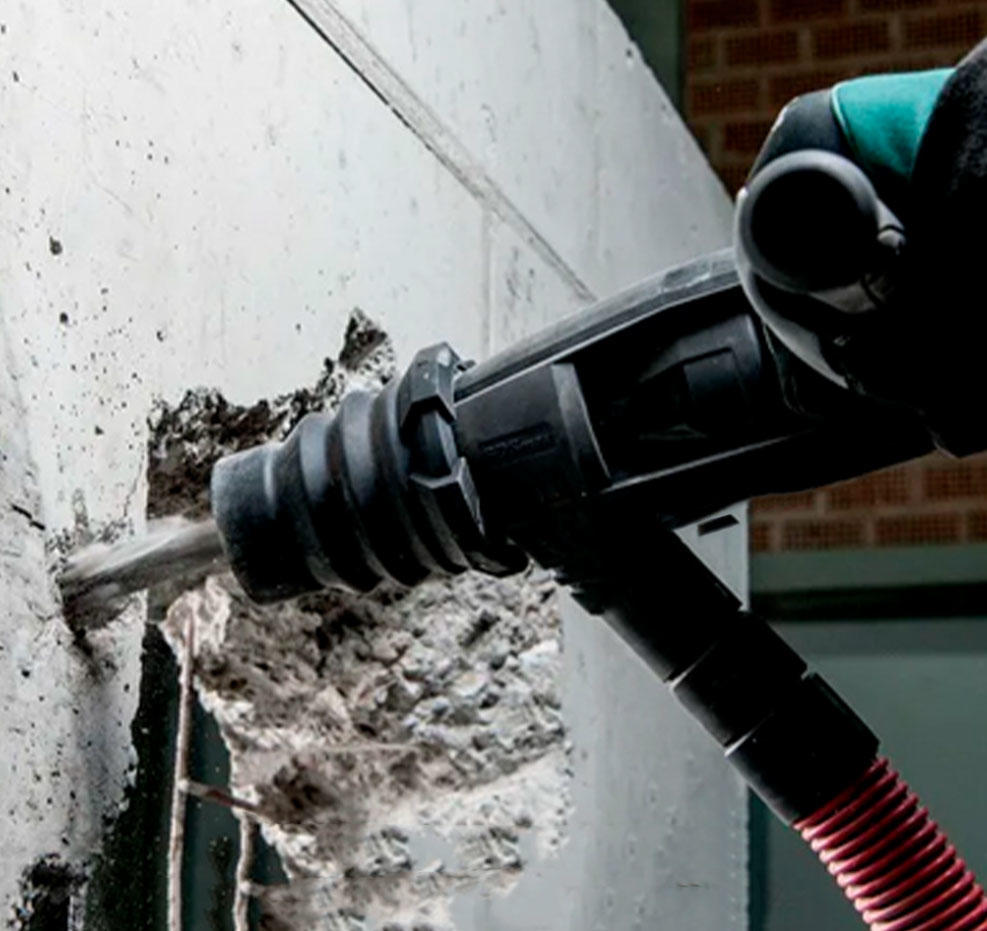
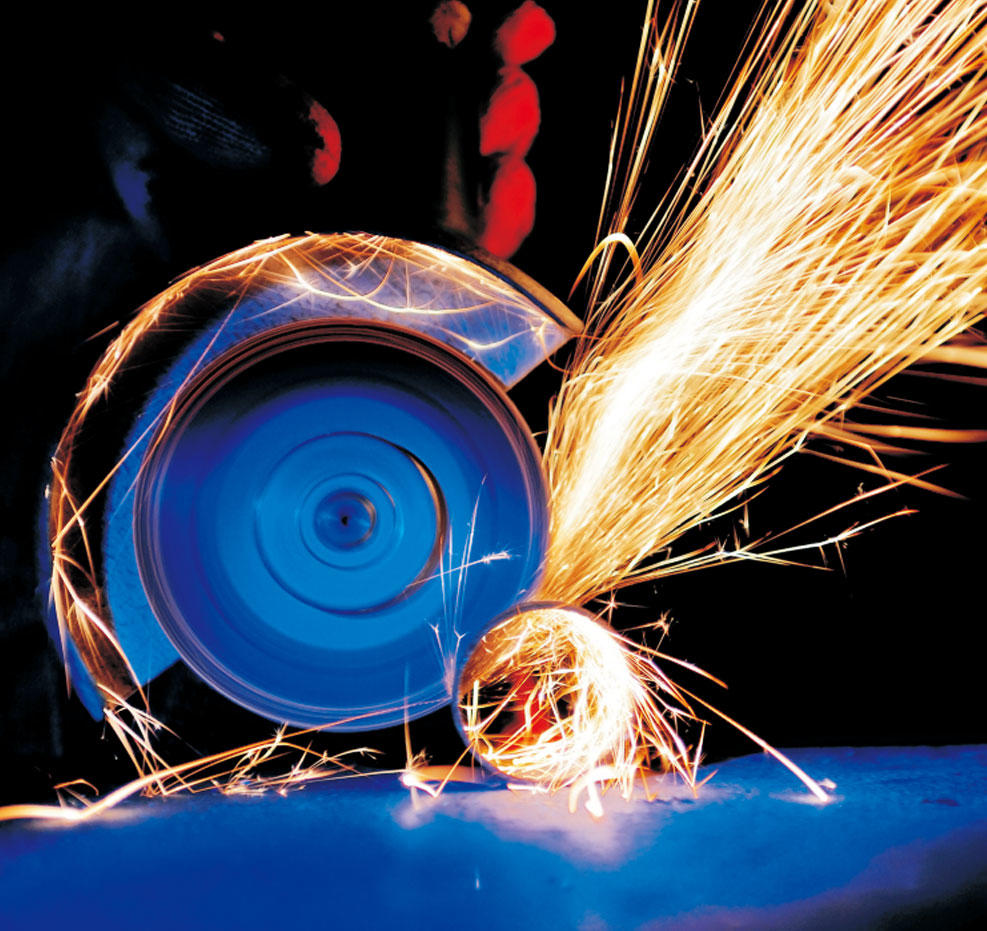
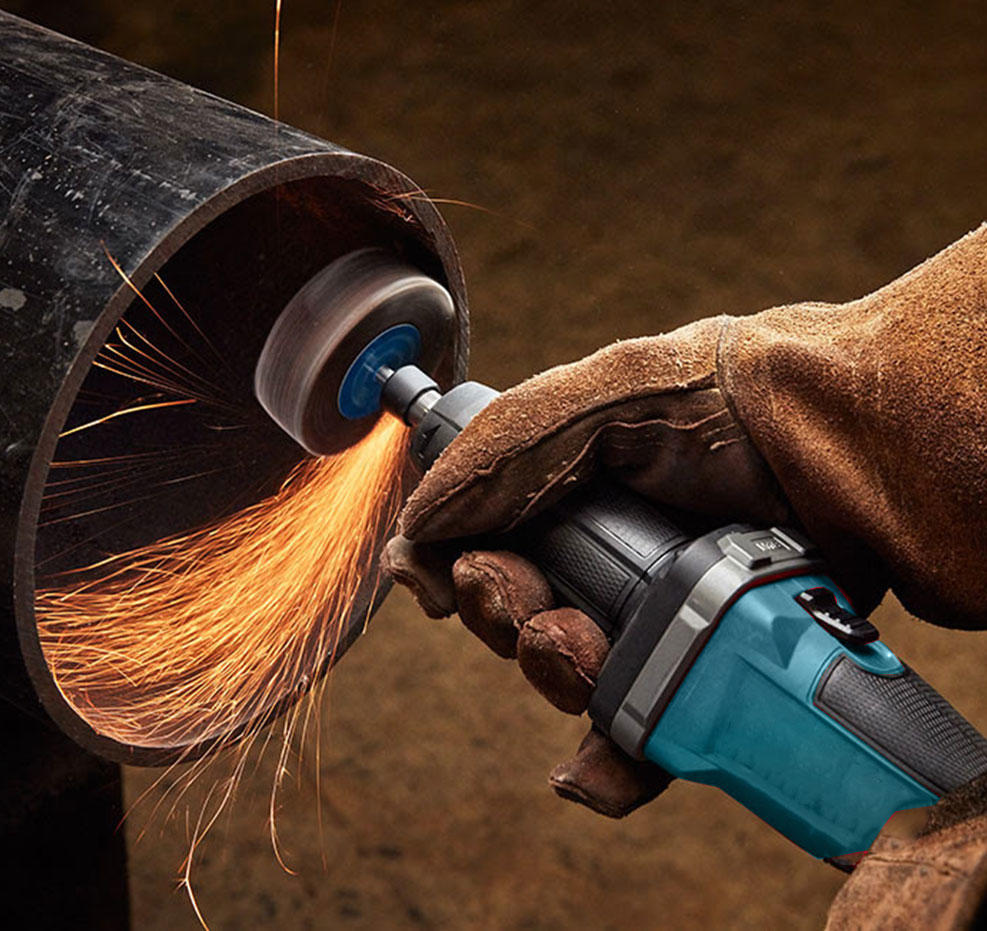
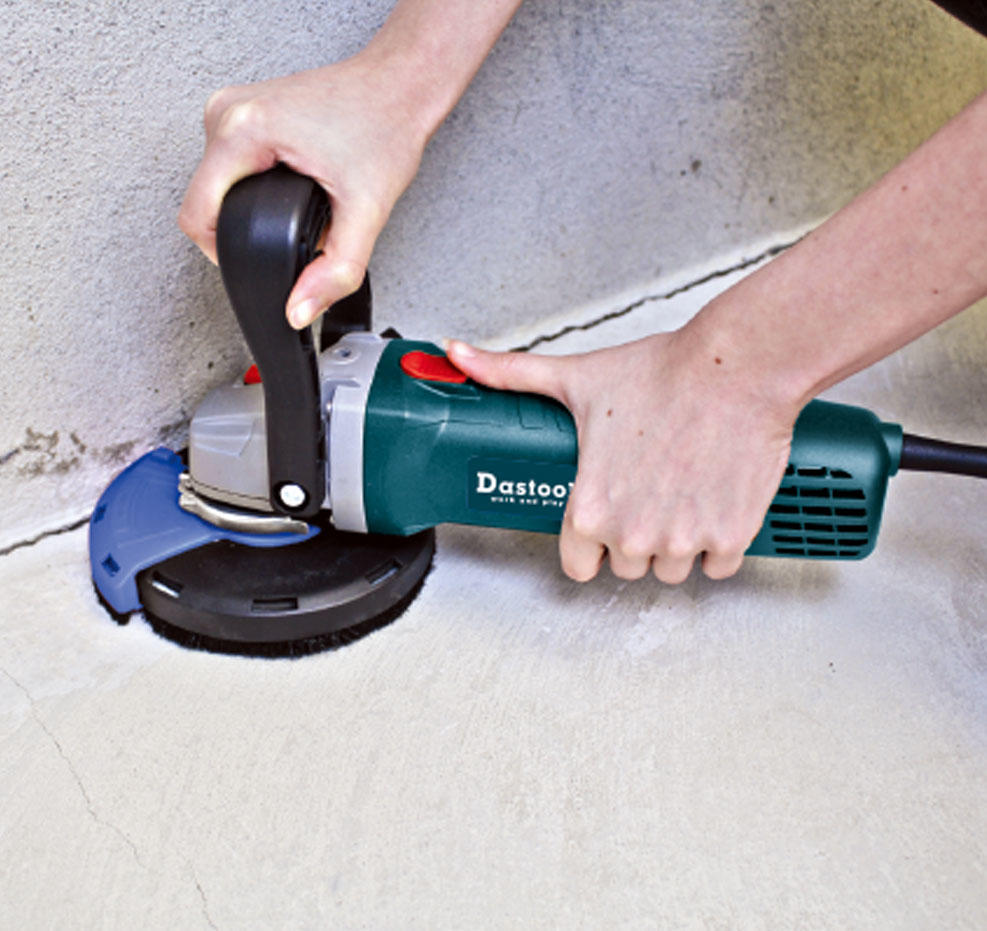
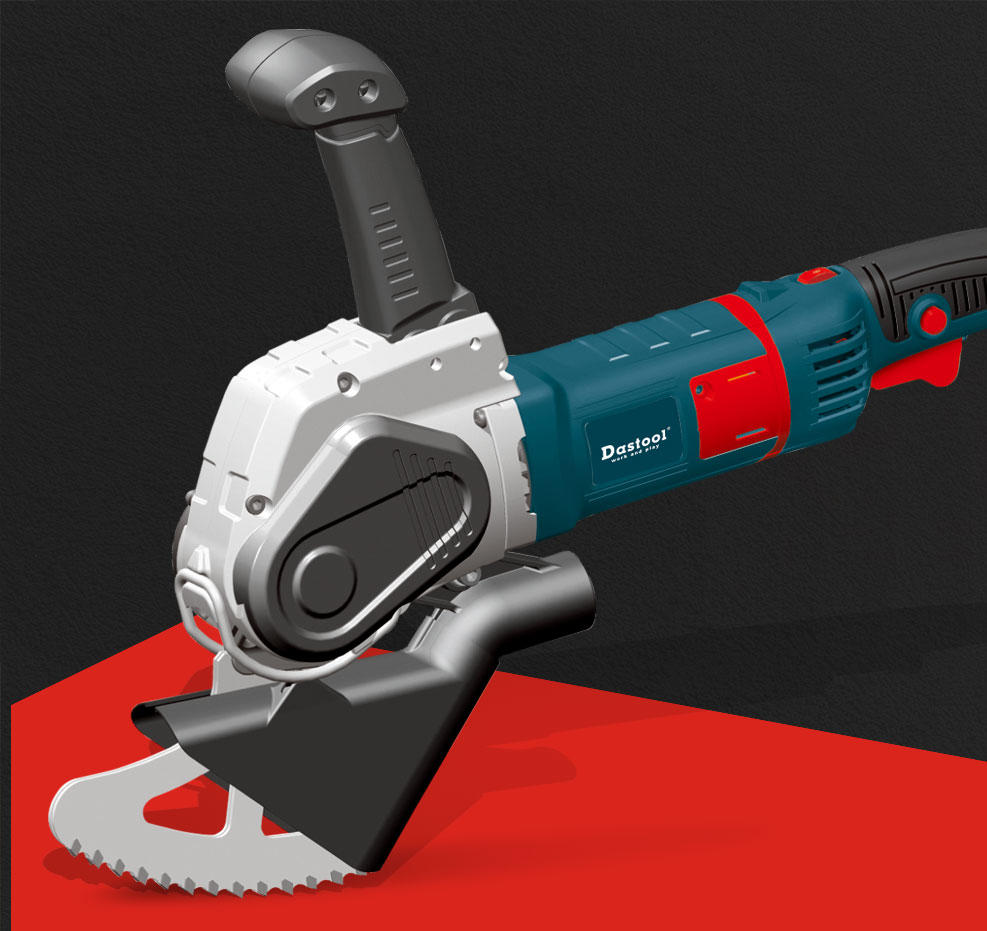
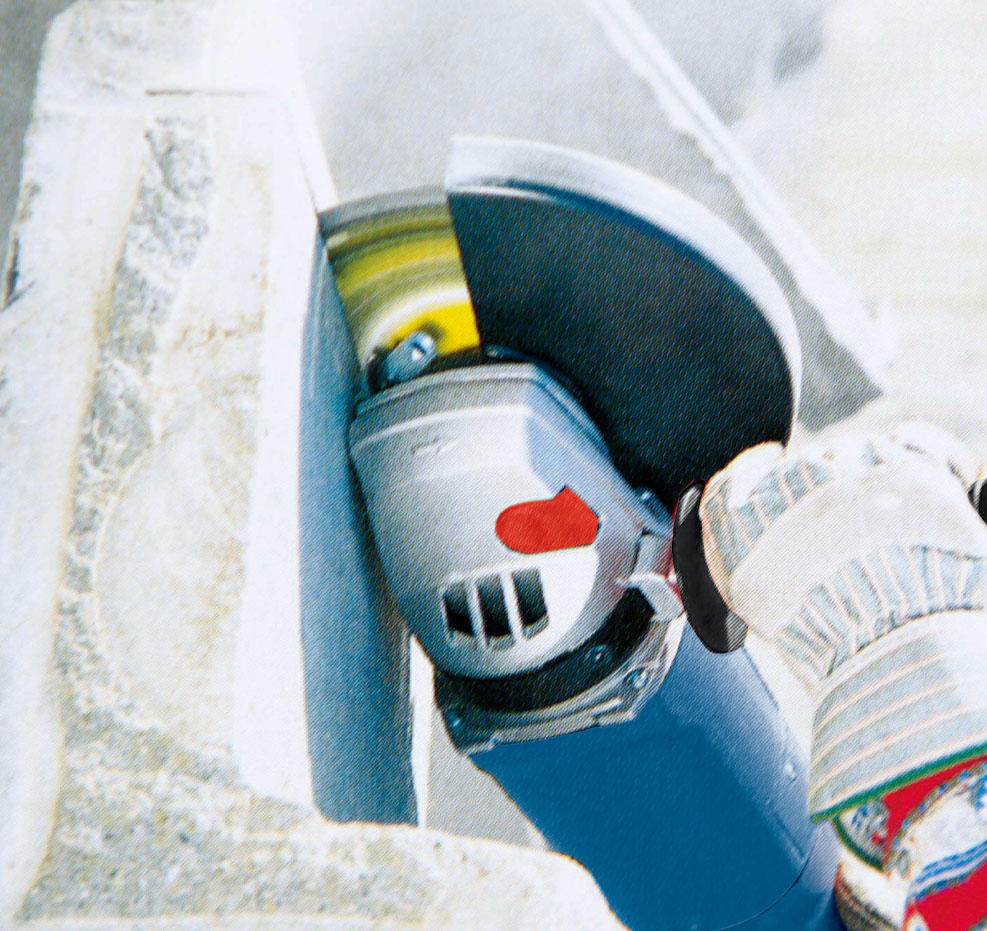
Grinders: Angle grinders are versatile tools for cutting, grinding, and polishing metal, tile, concrete, and other materials. They require caution due to their high-speed rotating discs.
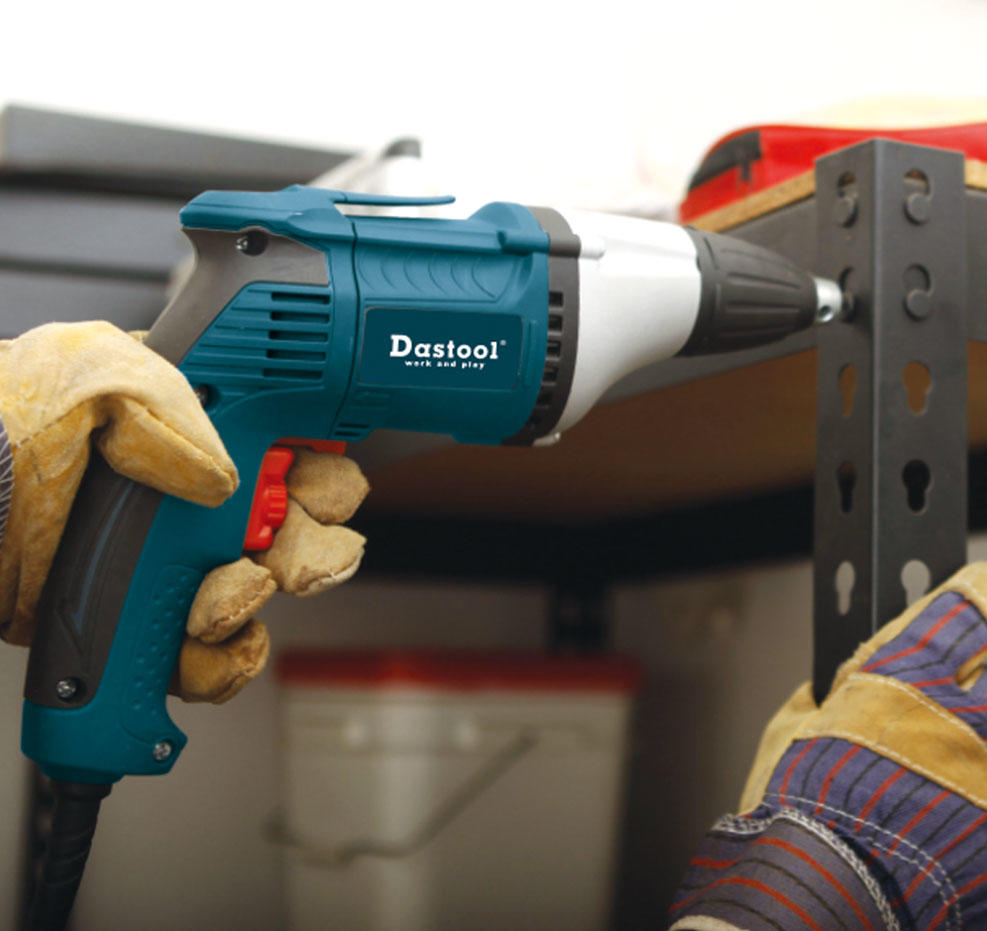
Power Screwdrivers: They make driving screws faster and easier. Power screwdrivers are available in corded and cordless models and are particularly useful for assembly work.
Planers: Planers are used to smooth or flatten wooden surfaces. They are commonly employed in carpentry and woodworking projects.
Safety Tips for Power Tool Usage:
Read the manual: Always familiarize yourself with the manufacturer's instructions and safety guidelines specific to the power tool you are using.
Personal protective equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, including safety goggles, ear protection, gloves, and dust masks, depending on the tool and task at hand.
Inspect tools: Before use, check power cords, switches, and blades for any damage. Ensure the tool is in good working condition.
Proper workspace: Create a clean, well-lit, and organized workspace. Remove any potential hazards or clutter that may cause accidents.
Electrical safety: When working with electric tools, use grounded outlets or a circuit with ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) to prevent electrical shock.
Secure workpieces: Ensure the material you're working on is securely clamped or supported to prevent unexpected movements.
Cord management: Keep cords away from sharp edges or heat sources. Use appropriate extension cords and avoid overloading them.
Proper grip and control: Maintain a firm grip on the tool with both hands, positioning yourself and others in a safe zone away from the tool's path.
Training and experience: Seek proper training or guidance before using unfamiliar power tools. Practice and gain experience to improve your skills.
Disconnect power: Before performing any maintenance, blade changes, or adjustments, disconnect the tool from the power source to prevent accidental starts.
Remember, power tools can be dangerous if mishandled or used without proper precautions. Always prioritize safety and exercise caution while working with these tools.
Power Tool Maintenance and Longevity: Cleaning, Lubrication, and Storage
Proper maintenance of power tools is crucial for their longevity and optimal performance. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and appropriate storage practices can help prolong the lifespan of your power tools. Here are some essential tips:
Cleaning:
Disconnect the tool from the power source before cleaning.
Remove any debris, dust, or residue from the tool's surface using a soft brush or cloth.
Pay special attention to vents, switches, and moving parts, as they tend to accumulate dust and debris.
For stubborn dirt or grime, you can use a mild detergent or specialized cleaning solutions recommended by the manufacturer.
Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that may damage the tool's surfaces.
Lubrication:
Lubricate your power tools regularly to reduce friction, prevent rust, and ensure smooth operation.
Check the manufacturer's recommendations for the appropriate lubricant to use.
Apply lubricant to the moving parts, such as gears, bearings, and joints.
Wipe off any excess lubricant to prevent accumulation of dirt or dust.
Blade and Bit Maintenance:
For power tools with blades or bits, such as saws and drills, keep them sharp and in good condition.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions for blade and bit maintenance, including sharpening and replacement.
Inspect blades or bits for any damage, dullness, or signs of wear. Replace them as necessary to maintain optimal performance and safety.
Electrical Components:
Inspect power cords for any fraying, cracks, or exposed wires. Replace damaged cords immediately.
Check switches, plugs, and connectors for proper functioning. Repair or replace them if they are faulty.
Avoid using power tools in wet or damp conditions to prevent electrical hazards.
Storage:
Store power tools in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area.
Use protective cases or toolboxes to protect your tools from dust, moisture, and physical damage.
Keep tools in their designated storage spaces to prevent entanglement or accidental damage.
If possible, store tools in a temperature-controlled environment to avoid extreme heat or cold, which can affect their performance and lifespan.
Regular Inspection:
Conduct periodic inspections of your power tools to identify any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction.
Look for loose screws, cracks in housing, or any unusual noises or vibrations during operation.
If you notice any issues, discontinue use and have the tool inspected or repaired by a qualified professional.



 English
English Español
Español